Why Solar?
Learn about solar energy
The power of solar energy is omnipresent. Discover the fascinating process by which solar panels capture the sun’s energy and convert it into electricity.
Solar 101
An overview of the origins and development of solar power throughout time.
In 1954, the initial silicon photovoltaic cell was created by Bell Labs. While there had been prior methods to capture and convert solar energy into usable power, it was only after 1954 that solar power started to emerge as a practical electricity source for long-term device usage. The first solar cells had an efficiency of 4 percent in converting solar radiation into electricity. To put things into perspective, contemporary solar panels widely available today have an efficiency above 20 percent, and this number continues to rise. Although the acceptance of solar energy was initially slow, a range of state and federal incentives and policies played a role in reducing solar costs, leading to increased adoption.

Essential information about solar energy that you should be aware of.
Solar power refers to the practical energy derived from the sun, which can be harnessed in the form of electricity or heat. There are multiple methods for capturing solar energy, with the most prevalent being the employment of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems. These PV systems convert sunlight into usable electrical power. In addition to photovoltaics, solar thermal energy, also known as concentrating solar power (CSP), is commonly utilized to heat indoor spaces or fluids. By implementing solar hot water systems and incorporating passive solar heating strategies into the design of residential and commercial buildings, property owners can fully optimize solar technology to leverage the sun’s energy efficiently.
Types of solar energy systems
If you’re interested in reaping the benefits of solar power, there are three primary scales at which solar panels can be installed: residential, commercial, and utility. Residential-scale solar is commonly implemented by homeowners through rooftop solar panels or ground-mounted installations on open land. The size of residential solar systems typically ranges between 5 and 20 kilowatts (kW), depending on the home’s dimensions.
On the other hand, commercial solar projects are typically larger in scale compared to residential installations. Although their size and cost can vary significantly, commercial-scale solar arrays serve the purpose of providing on-site solar power to businesses and nonprofit organizations.
Utility-scale solar projects, on the other hand, are typically extensive solar power plants with a capacity of several megawatts (MW). These installations aim to supply solar energy to a large number of utility customers.
For individuals who may not be able to install solar panels on their property due to financial constraints or other reasons, community solar offers a viable alternative. Community solar farms are constructed in centralized locations, allowing subscribers such as homeowners, renters, businesses, and nonprofits to participate in a shared solar project and enjoy the benefits of solar power without the need for individual panel installation.
How do solar panels work?
A solar panel, also called a solar module, comprises silicon cells, a metal frame, a glass casing, and wiring for electric current transfer. Silicon, an element with atomic number 14, possesses conductive properties that enable the absorption and conversion of sunlight into usable electricity. When sunlight strikes a silicon cell, it initiates the movement of electrons within the silicon, leading to the generation of an electric current. Referred to as the “photovoltaic effect,” this phenomenon forms the core principle of solar panel technology.
The process of generating electricity with solar panels can be simplified to the photovoltaic effect. Discovered by Edmond Becquerel in 1839, it represents a characteristic of specific materials, known as semiconductors, enabling the creation of an electric current when exposed to sunlight.
The photovoltaic process involves the following main steps:
- The silicon photovoltaic solar cell absorbs solar radiation.
- When sunlight interacts with the silicon cell, electrons are set in motion, resulting in the flow of electric current.
- Wires capture and channel this direct current (DC) electricity to a solar inverter for conversion into alternating current (AC) electricity.

What elements constitute a solar panel system?
Solar panel installations are simple and streamlined systems. They consist of only four essential components, which have no moving parts, making them highly efficient to install and upkeep. The four components of a solar panel system are as follows:
- Solar photovoltaic panels: These panels convert solar energy into electricity.
- Inverters: They convert the direct current (DC) electricity produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity.
- Racking and mounting systems: These systems securely attach the solar panels to either the roof or the ground, depending on the installation type.
- Performance monitoring systems: They enable tracking and monitoring of the output and overall health of the solar panels and inverters.

Solar panels
Solar panels are composed of a collection of silicon solar cells that are enclosed by a glass sheet and secured within a metal frame. These cells are equipped with wiring and circuitry, both inside and behind them, which enables the collection of electrical current generated by the solar cells. Each solar panel, also known as a solar module, typically measures around 4 feet by 6 feet and weighs approximately 30 pounds.
While solar panels lack moving parts, their essential component lies within the silicon cells themselves. When sunlight illuminates these cells, it triggers the activation of electrons, leading to the flow of electric current within the cell. The wires within the cells capture this electron flow, which is then combined with the output of other cells within the solar panel. For a more detailed understanding of the functioning of solar panels and solar cells, you can refer to our article on the subject.
Traditionally, solar cells are available in 60 or 72 cell formats. However, many companies are currently exploring innovative approaches to enhance the efficiency of solar cells in converting sunlight into electric current. As a result, you may now encounter “half-cut” solar panels, where each cell is halved, effectively doubling the number of cells on the solar module (e.g., 120 or 144 cells).
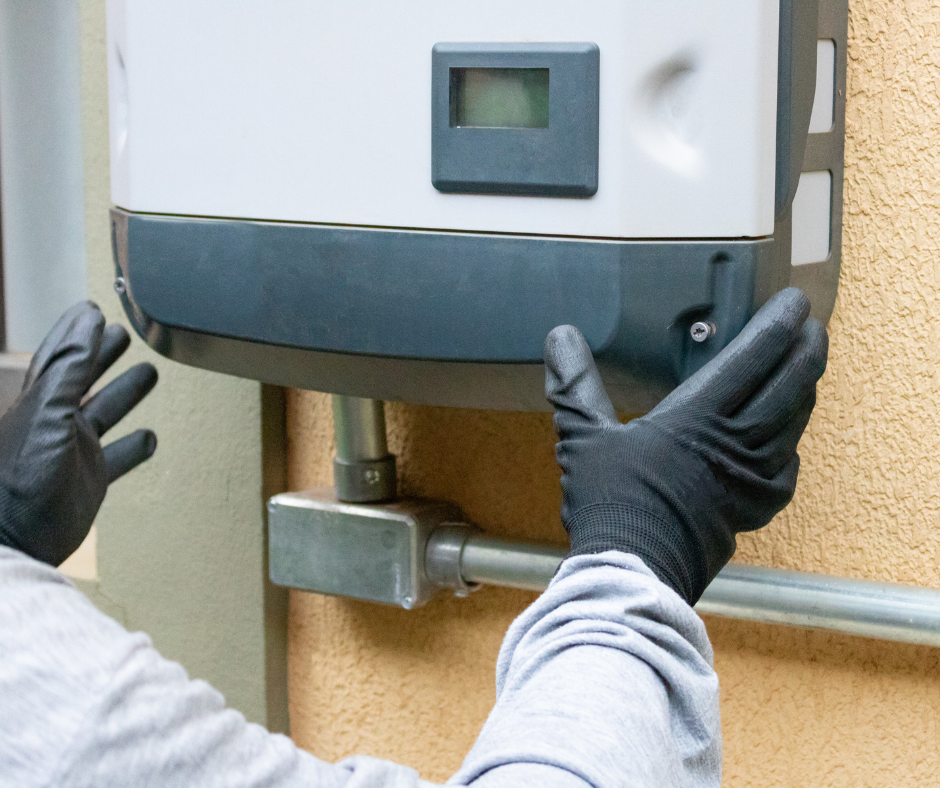

Inverters
The solar cells within your solar panels capture the energy from the sun and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. However, most homes and businesses utilize alternating current (AC) electricity. In order to make the DC electricity usable, inverters are employed to convert it into AC electricity. There are two primary types of solar inverters: string (or centralized) inverters and microinverters. It is also possible to combine power optimizers with string inverters to achieve similar functionality to a microinverter system.
String (or centralized) inverter: A single inverter connects your entire array of solar panels to your electrical panel. String inverters are commonly the more affordable option and have a long-standing history as the most widely used inverter type. Multiple strings of panels can be connected to each inverter. However, if the production of electricity from one panel in a string decreases, such as due to shading, it can temporarily affect the performance of the entire string.
Microinverters: With microinverters, typically one is installed at each solar panel, enabling maximum production from each panel. Microinverters are beneficial when panels experience shading at different times of the day or are not uniformly oriented. The cost of microinverters is usually higher compared to string inverters.
Power optimizers: Systems that incorporate power optimizers combine aspects of both microinverters and string inverters. Like microinverters, power optimizers are installed at each panel. However, instead of directly converting DC electricity to AC, the optimizers condition the DC electricity before transmitting it to a centralized inverter. Power optimizers perform well when one or more panels are shaded or have varying orientations. They generally have a higher cost compared to string inverters but are less expensive than microinverter systems.
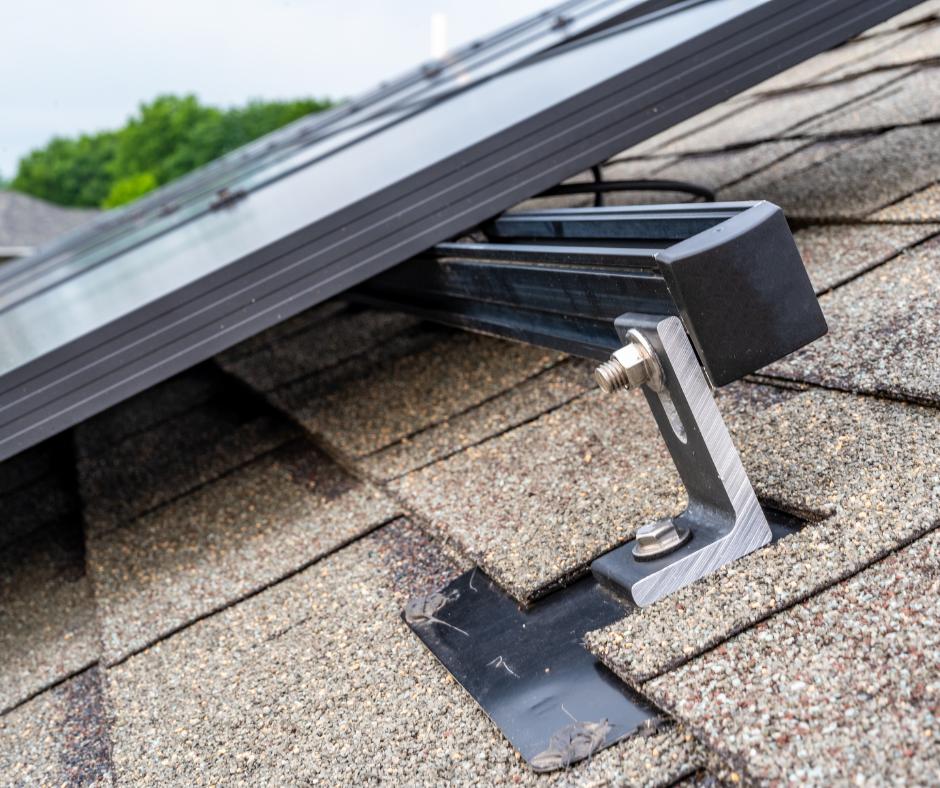

Racking and mounting systems
Solar racking and mounting systems are the hardware components responsible for securing your solar panels to either your roof or the ground.
For optimal performance, solar panels should ideally face south and be installed at an angle ranging from 30 to 45 degrees, depending on your distance from the equator. Panels facing east or west, with a pitch angle of five degrees or more, will still function effectively but may generate 10 to 20 percent less electricity compared to panels installed under ideal conditions. In residential solar installations, most roof-mounted systems use “lie-flat” configurations, aligning the pitch of the solar panels with that of the roof. However, in certain cases, racking can be used to tilt or position the panels at an angle that maximizes sun exposure.
There are two main types of mounts: fixed mounts, where the panels remain stationary, and tracking mounts, which enable the panels to follow the movement of the sun throughout the day (single-axis track mounts) and across different seasons (dual-axis track mounts). Tracker mounts are typically suitable for ground-mounted solar installations.
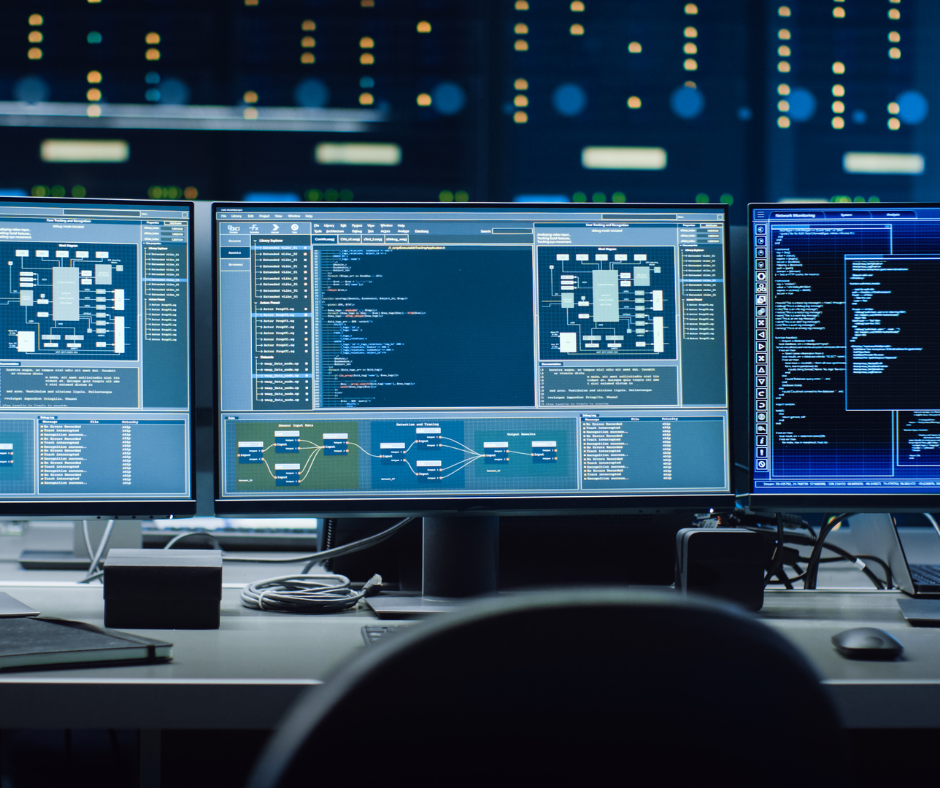

Performance monitoring systems
Performance monitoring systems offer detailed information about the operation of your solar panel system, allowing you to closely monitor its performance. With a monitoring system in place, you can measure and track the amount of electricity generated by your system on an hourly basis.
Most commonly used residential inverters come with production monitoring apps that enable you to monitor the output of your panels. In some cases, the app may also provide consumption monitoring, allowing you to track the overall savings from your solar panel system. It’s worth noting that this additional consumption monitoring may involve an additional cost.
By monitoring your solar panel system, you can identify any potential performance issues and take necessary steps to maximize electricity production and financial returns from your solar panel system.
There are two main types of monitoring systems:
On-site monitoring: In this type, the monitoring device is physically installed on your property and records the amount of electricity generated by your system.
Remote monitoring: With remote monitoring, your solar PV system transmits its performance data to a monitoring service that can be accessed online or through a mobile device.
The price of solar energy
As solar efficiency has risen, the price of solar panels has significantly decreased. Over the past decade, the cost of installing solar panels has dropped by more than 70 percent, and numerous experts in the industry anticipate further price reductions in the future.

Moreover, depending on your location, there are various rebates and incentives available for solar power that can further reduce its cost. Nationally, the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is a significant incentive accessible to those interested in solar energy, enabling a deduction of 30 percent of the solar array installation cost from federal taxes. However, it is important to note that this incentive is time-limited: in 2033, the federal ITC decreases to 26 percent, and for residential solar installations, it will be completely phased out by 2035. Additionally, many states and utility companies provide additional incentives, such as net metering, which further decrease the expense of solar power.
If you are curious about the cost of solar for your specific situation, you can use our solar calculator for a quick estimation.
Solar energy is an example of a renewable energy resource
Solar energy is an environmentally friendly and cost-effective renewable power source that can be harnessed in almost any location worldwide. Any place where sunlight reaches the Earth’s surface holds the potential to generate solar power. Since solar energy originates from the sun, it represents an inexhaustible source of power. In contrast, fossil fuels, such as oil, gas, and coal, which took hundreds of thousands of years to form, are finite resources that deplete with every instance of their combustion to produce electricity, along with associated emissions. In contrast, renewable resources like wind, solar, and hydropower do not deplete when utilized to generate electricity. Sunlight will consistently shine on Earth’s surface, ensuring an endless supply of sunlight for future electricity production. This intrinsic characteristic of solar power makes it a renewable energy source.
Although the current electricity mix in the United States still heavily relies on fossil fuels, renewable energy sources like solar are progressively gaining a larger share in the country’s energy portfolio as their costs become more competitive.

Should you go solar?
When it comes to transitioning to solar panels and adopting an environmentally friendly energy source, there is no universal solution that fits every situation. To determine if your home or business is suitable for solar energy, there are several important questions to consider:
What is your electricity consumption and the cost of electricity in your area? The higher your electricity usage and rates, the greater the potential savings from switching to solar power.
Do you own your home? Installing solar panels is more challenging for multi-family or rented properties compared to single-family homes that you own.
Is your roof suitable for solar installation? An ideal roof for solar panels would have sufficient space, be in good condition, have a simple design, face south, and receive ample direct sunlight. If not, you can explore the possibility of a ground-mounted system if you have available land space.
Are there reputable local solar companies in your area that can handle the installation? If you are in an area with limited installers, it may result in higher costs.
What incentives are available in your location? Local and state incentives can significantly reduce the cost of your solar energy system and shorten the time it takes to recoup your investment.
If some of these factors do not align with your circumstances but you still have an interest in solar power, you can refer to our article on whether solar is the right choice for you to gather more information and determine if it suits your needs.
Understanding the solar industry: Key information to consider
According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), solar capacity has experienced an average growth of approximately 33 percent over the past ten years. In the United States, the Department of Energy (DOE) reports a current installed solar power capacity of around 97.2 gigawatts (GW), which is sufficient to supply clean energy to approximately 18 million households.
As the solar capacity continues to expand, the demand for new job opportunities in the solar industry also increases. Various roles, including installation, manufacturing, operations and maintenance, and consumer education, offer diverse employment prospects. As of December 2021, the solar industry supported 255,037 jobs, marking a 9.2% growth compared to 2020, as reported by the National Solar Jobs Census conducted by the Interstate Renewable Energy Council (IREC).
The widespread adoption of solar power both domestically and globally has also led to significant growth in related sectors. Solar battery systems, electric vehicles, and heat pumps are prominent examples that are expected to flourish alongside the solar industry, enhancing the advantages of solar energy.
If you wish to contribute to the growth of the solar industry, one way is to consider switching your electricity source to solar power. Whether it involves installing solar panels on your property or participating in a community solar farm, you will contribute to the overall installed solar capacity while supporting the expansion of the clean energy economy.
What Our Clients Are Saying

Solar Experts Northeast Atlanta was a great choice for my family. Their team of experts provided amazing service and we're already saving money on our monthly energy bills!


I was hesitant about switching to solar, but Solar Experts Northeast Atlanta made the process easy. Their customer service is top-notch and I'm so happy to be contributing to a cleaner environment.


Very professional and best prices!


Choosing Solar Experts Northeast Atlanta was the best decision I made for my solar installation needs. From the moment I contacted them, their exceptional service and expertise shone through. The team at Solar Experts Northeast Atlanta went above and beyond to ensure that I had a seamless experience throughout the entire process.


I wholeheartedly recommend Solar Experts Northeast Atlanta to anyone considering solar installation. Their excellent services, knowledgeable team, and unwavering commitment to customer satisfaction make them the go-to choice for all solar needs. Thank you, Solar Experts Northeast Atlanta, for your exceptional work!


What truly sets Solar Experts Northeast Atlanta apart is their ongoing support and dedication even after the installation was complete. They have been readily available to address any post-installation queries and have provided valuable advice on maximizing the benefits of my solar system.


Their knowledge and professionalism were truly impressive. They took the time to understand my energy needs and provided me with a customized solar solution that perfectly suited my requirements. They patiently answered all my questions, addressing any concerns I had, and guided me through the entire installation process.


The installation itself was carried out flawlessly. The team was prompt, efficient, and extremely respectful of my property. They worked diligently to complete the project within the agreed-upon timeframe, ensuring minimal disruption to my daily routine.


I recently had the pleasure of working with a reputable solar energy company, and I must say that choosing them was a fantastic decision for my family. Solar Experts Northeast Atlanta proved to be a reliable and professional team of experts who went above and beyond to provide exceptional service.

Contact Us

Need A Free Estimate?
Find out how much you can save with Solar Experts Northeast Atlanta